How Mendelian Segregation of Alleles at Multiple Loci Generates Continuous Phenotypic Variation
Multiple alleles are a pattern of inheritance that is a non-Medellin type and consists of two alleles in general.
It has more than just the general two alleles that can code for a specific trait in species. Some multiple alleles example is the-
- Multiple alleles example in plant
- Multiple alleles example in human
- Multiple alleles example in animal
- Multiple alleles example in blood
With this concept and the multiple alleles example in mind, there are more than only one phenotype that is seen and depends on the recessive or the dominant alleles that are seen in the character and the pattern of dominance for the individual and then allows the follow up when gets combined together. Gregor Mendel only took the understanding of the trait in the pea plant showing dominance with two alleles.
Those two allele can be multiple alleles example and contribute to having only one trait in the plant being shown. It was till this that was found telling that some characters can also show more than two alleles that shall code for the phenotype. This allowed the rise of many phenotypes to be seen for any particular trait while still the Mendel's law was being followed. There is always a mixture coming to act when there is a multiple allele. At some point, the one of the two alleles can be seen to be recessive.
On being so, to the rest and shall be masked out by any of the other one that are called to be dominant. The rest of the alleles shall be co-dominant in group and then show the character that is same as phenotype of that to the person. There are many more cases where the few alleles shall show incomplete dominance and shall be put with the genotype. A person shall have this type of inheritance linked to the multiple alleles and multiple alleles example and can blend with the phenotype that shall mix with both the alleles and trait together.
What is multiple allele?
The word "allele" is a short form of allelomorph which was used in the early days of genetics to describe variant forms of a gene detected as different phenotypes.
An allele is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides that encodes the synthesis of a gene product at the same place on a long DNA molecule. At the lowest extreme, an allele can be based on a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). At higher extremes, it can be based on differences up to several thousand base-pairs long.
Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles.
A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. Allelic variation at a locus is measurable as the number of alleles (polymorphism) present, or the proportion of heterozygotes in the population. A null allele is a gene variant that lacks the gene's normal function because it either is not expressed, or the expressed protein is inactive. Other disorders are also due to recessive alleles, but because the gene locus is located on the X chromosome, so that males have only one copy, they are more frequent in males than in females.
Multiple alleles example in plants
Plants are the organism that can be exemplified to be the herbs, grass, mosses, trees that absorb water.
We have widely seen that the shape of a potato is tuber and this is continuous with having a phenotype that is visual like being round, long tuber and can be discerned to be at the level of being diploid.
This is a multiple alleles example for plants that many experiments proof show that the presence of the system for multiple allele is being seen for the first time. The allele that is recessive for the tuber shape can be said to be as quantitative and recognized to the near view allele. Variation between the alleles is common and the dominant shall be visible that shall be seen.
The view that most of the allele that are recessive offer shall be said to be a near null or whole null allele and shall be consistent with the number of effects in regards to quantity they shall offer at the locus and can be described. When the metric tuber in addition to it is resolved in the Mendelian factor that uses the heterozygous parent in the designed experiment have conclusions like that change the relative vitality of the multiple alleles and multiple alleles example to loci explaining the genes.
Multiple alleles examples in animals
There can be two of the example defined here. One can be the coat color of the animals and other can be regards the insects.
For many years the domestic cats have been bred for coating. The gene determines the color of them and appears to have multiple variants as the coat ranging from brown white and black.
This implies thatmultiple alleles decide the color of the coat. The color of the coat has gene that has multiple alleles in population and the pigment that makes the protein is based in inheriting of it and getting to express the alleles. Other genes start to regulate the curliness, patterns and even the texture along with the shading in the same manner. The number of combinations possible is many and then get to express them in distinct genotype from these resulted alleles.
The result is conversed to wide area and also a lot of breed. Even when the only four of the alleles tend to share them between the two parents for each of the gene the variation is separate and good. The color of the coat implies multiple alleles example and appears to have more than two of the alleles present for the phenotype of coat color.
On the other hand, in base way the genotype of cat can be said to be seen by getting the cat examined for its color and the color pattern. If the phenotype of the parent are called then it is usually seen that the color possible for the kitten via calculation shall be much complex in many cases. This means the orange and black or grey or white and the patches tend to be white.
An insect called to be Drosophila melanogaster which is called the fruit fly had a complex genome. They are prone to the lab words and for its high reproduction and ease can be kept for analysis. They are smaller than human. Humans have 23 chromosomes but flies have 4 of them. The wings of them are long. There were two mutations that had taken place in the same locus that resulted in the less wings and other having less but developed wings.

When the fly having the vestigial wings shall be crossed with other and then altered wings the resulting in the F1 hybrids shall have intermediary wing length and shall imply that none had been mutated with the dominant genes. On occasion it can be said that the vestigial compound, the hybrid shall have two of the genes mutated at the same locus. The Mendelian segregation and the evident recombination is clear here.
Multiple alleles example in blood
There can be quite a fewmultiple alleles example and can vary from plants to humans and shall be based on the Mendel law.
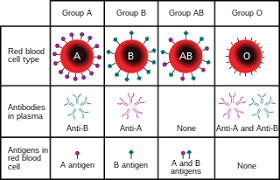
The best multiple alleles example for blood is the ABO blood group. Humans tend to have red blood cells and are of the type A (I A), type B (I B), or type O (I). These are said to of three separate alleles and can link in several ways to follow the Mendel law.
The genotype is the outcome and shall be of wither the type O, type A, type B or of type AB. Type A group is the link of either the two alleles f A, IA IA or with one of A and the one of 0. Along with this, the same goes for B blood which is coded only to take the two of the recessive alleles of O (II). This is a good multiple alleles example and also a simple dominance. The type of AB is said to be co-dominance.
Both the alleles B and allele A are same in its dominance and shall be able to easily express itself while being paired in linkage. Both the allele being same in dominance shall express the genotype of when paired together. Neither the B or the A allele shall be dominant over each and thus this type if actually expressed in the phenotype that shall give the human a blood type of AB.
All for the humans and many primates can have its type of ABO blood. There are four in general. Blood O is the common among them. On getting wrong group of blood from people can lead to death. Just for instance if person having a group of blood being B takes in A type then one having antibodies of anti-A shall attack the cells of the type A. this is the example of the group A blood and shall never be given to some having the group B and also vice versa.
Multiple alleles examples in humans
There are few traits in humans that shall lead to having of more than two alleles types.
The trait that has there or much more of the alleles shall be referred to having of multiple alleles. The human shall have the ABO group system and also the eye color.
The three of the alleles are the A (IA), allele B (IB), and allele i (IO or i). If allele A is seen on chromosome, then protein A is made and the red blood cells of the person shall have protein A on its membrane. If the chromosome shall have a B allele, the protein B is seen. At last, if the I allele is seen on any chromosome nether the protein B or protein A shall get synthesized. These are the three alleles shall make up the ABO blood system or trait.
The pattern for the allele B and alleles A sow co-dominance. It takes place when neither of the alleles are dominant over any and the individual that is heterozygous shall be able to express both of the phenotypes. This implies that if any individual has an allele A on any one of the chromosome and allele B on the second pair of chromosome then both the proteins shall be expressed and the RBC shall have protein B or A on the cell.
There are many of the population that has three alleles and each of them shall inherit only two of them from the parents. This is the outcome in the genotype and shall depict each trait that is inherited from parent. If there are three alleles there shall be 6 genotypes and the number of phenotype shall decide the dominance between the 3 alleles. The ABO blood has four phenotypes and thus a good multiple alleles example.
Can a gene have multiple alleles?
There are traits in humans and other organisms that have three or more different types of alleles or genes. When a trait has three or more distinct alleles, it is referred to as multiple alleles inheritance.
Although individual humans and all diploid organisms can only have two alleles for a given gene, multiple alleles may exist in a population level, and different individuals in the population may have different pairs of these alleles.
Multiple alleles example means that there are more than two phenotypes available depending on the dominant or recessive alleles that are available in the trait and the dominance pattern the individual alleles follow when combined together. Human blood is controlled by three alleles that create the ABO blood types. A and B are co-dominant, while the third allele, O, is recessive to the other two alleles. Below are a number of parent combinations. For each, indicate whether it could produce the resulting child.
The word allele is a general term to denote the alternative forms of a gene or contrasting gene pair that denote the alternative form of a gene is called allele. These alleles were previously considered by Bateson as hypothetical partner in Mendelian segregation. In Mendelian inheritance a given locus of chromosome was occupied by 2 kinds of genes, which is for a normal gene (for round seed shape) and other its mutant recessive gene (wrinkled seed shape). But it may be possible that normal gene may show still many mutations in pea besides the one for wrinkledness.
If we assume that these mutant genes, vestigial and antlered are not allelic located at different loci in place of locating at same locus in different chromosomes so closely linked that there is no crossing over between them, the mutant gene will suppress the expression of adjacent normal allele to certain extent. These closely linked genes are called pseudo alleles and this suppression is the result of position effect. Thus, visible or apparent cases of allelism may be explained on the assumption of close linkage.
Is multiple alleles an inheritance pattern?
Multiple alleles is a type of non-Mendelian inheritance pattern that involves more than just the typical two alleles that usually code for a certain characteristic in a species.
It refers to the quantitative inheritance wherein two or more independent genes additively affect a single phenotypic trait. In a way, polygenic inheritance is a multiple factor inheritance or multiple gene inheritance, or multifactorial inheritance.
In case of multiple alleles, the same DNA strand is involved, whereas polygenic inheritance is found on multiple DNA strands. Multiple alleles involve multiple alternate forms of a gene, while polygenic traits are regulated by a group of non-allelic genes. An inheritance of a character that depends upon the cumulative action of many genes, each of which produces only a small effect. Examples of such quantitative characters include spore production in ferns, height of trees, and nectar production in buttercups.
Eye color is a multiple alleles example. They are more than two alleles encoding for the same. he key difference between codominance and multiple alleles is that codominance is expressing the effects of both alleles independently, without blending in the heterozygous state, while multiple alleles refer to the state of a trait that has more than two different alleles. a person inherits one allele from his or her mother and one allele from his or her father.
Therefore, individuals with an autosomal recessive single-gene disease inherit one mutant allele of the disease-associated gene from each of their parents. n the most elementary form, the inheritance of eye color is classified as aMendelian trait. On the basis of the observation of more than two phenotypes, eye color has a more complex pattern of inheritance. Eye color ranges include varying shades of brown, hazel, green, blue, gray, and in rare cases, violet and red.
Source: https://lambdageeks.com/multiple-alleles-example-2/
0 Response to "How Mendelian Segregation of Alleles at Multiple Loci Generates Continuous Phenotypic Variation"
Post a Comment